
Minor-degree changes are much easier to incorporate into the existing routine, making it sustainable and consistent. Berkowitz Pollack Brant has cultivated a diverse client base that includes companies of all sizes. The incremental volume change is how much extra output is being proposed or considered for evaluation. Continuing the example, let’s say it costs $100,000 to produce the 10,000 units in a typical month. For example, if you normally produce 10,000 units of a product per month, this base monthly volume is 10,000 units.
FAQs about Incremental Cost: Definition, How To Calculate, And Examples
Incremental cost refers to the change in total cost resulting from a specific decision or action. It helps businesses and individuals evaluate the financial impact of their choices. A software development company is deciding whether to bookkeeping invest in upgrading their existing infrastructure. Through incremental cost analysis, they assess the additional expenses of purchasing new hardware, software licenses, and training employees. By comparing these incremental costs with the anticipated benefits of improved efficiency and productivity, they can make an informed decision about the feasibility of the upgrade.
What Are the Two Stages of Allocation in Activity-Based Costing?
Remember, every decision involves trade-offs, and understanding these limitations enhances our decision-making process. Incremental analysis provides a structured framework for decision-making. By focusing https://www.bookstime.com/articles/what-are-income-statement-accounts on the changes brought about by a specific choice, managers can evaluate options objectively. Whether it’s a small operational decision or a major strategic move, incremental analysis helps navigate the complexities of business with clarity and precision. Remember, the devil is in the details, and incremental analysis helps uncover those crucial details that drive smart decisions.
- Profitable business decisions include knowing when is the best opportunity to produce more goods and sell at a lower price.
- Optimizing labor allocation and investing in training can enhance productivity and reduce costs.
- Direct materials are the tangible inputs required to produce a product and are directly proportional to production volume.
- In this section, we will delve into the practical application of incremental cost analysis by examining real-world case studies.
- A specific material used in production is a variable cost because the price changes as you order more.
Direct Materials

Yet, when you trace the most significant and successful endeavor initiated by the organization, it will be these minute, minimal changes made. This approach comes with minimal effort and delivers the most significant result, allowing teams to make consistent and small steps. Incremental improvement is an effective way to drive business success in the long term. This approach draws inspiration from the theory of marginal gains, which suggests that a 1% improvement in the performance of each task, creates a positive overall impact.
Incremental cost and its effect on pricing
- Doing more with limited resources is the core of incremental improvement.
- This allows the team to focus on tasks that matter and require their attention.
- Thus they realized that they have incurred considerable incremental costs apart from baseline cost which does not reflect favorably on overall project implementation.
- The basic method of allocation of incremental cost in economics is to assign a primary user and the additional or incremental user of the total cost.
- Through incremental cost analysis, they assess the additional expenses such as rent, utilities, and staffing required for the new store.
- Accurate tracking of these costs ensures compliance with financial reporting standards and precise inventory valuations.
These must be overcome with consistency in improvement habits and fixed processing structure. Employee engagement is a key factor that ensures better processing and operational excellence. To drive employee engagement, it is important to keep them motivated and recognized. This is where incremental improvement initiatives deliver the intended upgrades. Employees are empowered to improve their tasks and find solutions that they think are beneficial to the servicing.
- By acknowledging these limitations, we can make more informed choices in the complex landscape of business decisions.
- Incorporating incremental cost in business strategies offers several benefits, including improved decision-making, cost optimization, resource allocation, risk assessment, and enhanced profitability.
- To drive employee engagement, it is important to keep them motivated and recognized.
- By analyzing these incremental costs, the firm can allocate its resources effectively and maximize returns.
- Production costs for one part would include the employee’s rate of pay (calculated hourly) plus the cost of all the materials used to produce a part or unit.
As a result, the total incremental cost to produce the additional 2,000 units is $30,000 or ($330,000 – $300,000). The first step forward is incremental cost analyzing the current status of the processes and their drawbacks. This can be done through proper assessments to identify areas of improvement. For starters, it is ideal to focus on smaller and gradual changes that could significantly change the trajectory and efficiency of the processes, making them productive and sustainable. Most business leaders and decision-makers look forward to radical changes that will bring an immediate surge in processing and operational excellence.

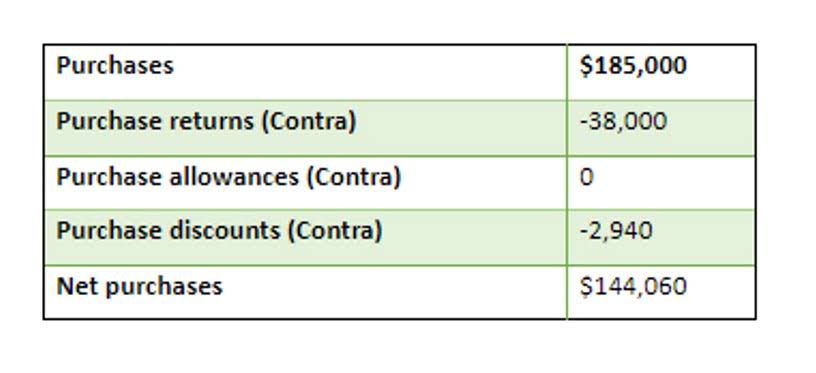
Applying this methodology to your business decisions yields pivotal insights for profitability and strategy. Thus, we see that factors taken into consideration in this concept are those that change with production volume. The fixed costs are not considered over here because they remain the same.
- There will be instances where bigger issues have to be solved with bigger initiatives, however, most often these bigger issues could have been dislodged with simpler and minute changes at the onset.
- So remember – instead of maximizing profits through deceitful tactics creating values that meet customers expectations is key.
- When faced with complex business decisions, managers often find themselves at a crossroads.
- By staying true to the core model/structure, Apple has been gradually refining product specifications and innovation methods, and creating impactful improvements.
- Alternatively, once incremental costs exceed incremental revenue for a unit, the company takes a loss for each item produced.

The company must weigh these incremental costs against the projected revenue from the new product line to decide whether it’s a profitable venture. Incremental costs change at different scales of production, and so do their benefits. Businesses must determine the exact volume at which they can get the greatest value. The expense of subcontracting a particular service includes the additional costs incurred by a firm that are not present when those services are provided in-house. This expense includes costs such as labor fees, supervision expenses, and related taxes. It is important to carefully assess the advantages versus the disadvantages of outsourcing before making a decision.
